SACA Welcomes New Executive Program Director
The Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA) is pleased to welcome Sue G. Smith as its new Executive Program Director. Smith joined SACA in May 2024 after working at the highest levels within Indiana’s Ivy Tech Community College for more than 30 years.
During her tenure with Ivy Tech, Smith developed expertise in consulting; workforce and economic development; program and partnership development; and advanced and smart manufacturing. Most recently, she served as Vice President of Ivy Tech’s award-winning School of Advanced Manufacturing, Engineering, and Applied Science (AMEAS).
At Ivy Tech, Smith prioritized strengthening programs with an eye toward economic and workforce development. In particular, she worked extensively with employers throughout Indiana and neighboring states to ensure the programs in the School of AMEAS aligned with industry needs.
Under Smith’s leadership, Ivy Tech’s School of AMEAS grew to be a major economic development resource for Indiana. It also became the first college in the United States to develop and deliver a smart manufacturing degree called Smart Manufacturing Digital Integration (SMDI).
Ivy Tech’s SMDI degree was based upon SACA credentials that were vetted with manufacturing employers. The SMDI degree has been especially attractive to new industries looking to move into Indiana, since advanced automation skills are critical for cutting-edge technologies used in electric battery, electric vehicle (EV), semiconductor, and biopharmaceutical manufacturing.
The success of Ivy Tech’s School of AMEAS and its groundbreaking SMDI degree has captured the attention of not only other community colleges and universities around the country, but also organizations around the world. In fact, Smith recently delivered a keynote address at the European Educational Congress in San Sebastian, Spain, on smart manufacturing and the implementation of embedding SACA credentials stacking into programs.
SACA Executive Director Jim Wall is excited to see Smith use her experiences at Ivy Tech to help other organizations build similar programs. According to Wall, “SACA’s been growing pretty dramatically in the last two years, so we needed to bring in a nationally-known leader in education and industry. We’re very proud and fortunate to say that Sue Smith has come on board as our Executive Program Director.”
Wall notes that “Sue’s primary responsibility is going to be helping to grow SACA membership by being a resource for instructors and administrators across the country. She’ll also be working with some of our industry partners to help them develop pathways internally for their employees that can utilize SACA certifications.”
Smith says, “I’m really excited to be with SACA.” Reflecting on her journey from Ivy Tech to SACA, Smith notes that “as I rolled that [SMDI] out at Ivy Tech, I got tons of calls from other community colleges and organizations saying, ‘Hey, how did you do this? Can you do this for us?’ So, when this position came up, I thought, ‘Yeah, I think I can do that for other schools and other industries.’”
What does Smith hope to accomplish with SACA? “I’m trying to accomplish that sort of ‘high tide raises all boats,’ if you will. I’m trying to make this opportunity available for employers and for community colleges and universities in any state.”
About SACA
SACA sits at the forefront of the effort to certify students and workers who demonstrate the required knowledge and hands-on smart automation skills employers so desperately need. SACA’s certifications were developed in conjunction with industry partners who could speak from experience about their needs when it comes to workers able to work alongside a variety of advanced automation technologies.
SACA offers a wide variety of certifications in popular industrial skill areas, including certifications at the Associate, Specialist, and Professional level. For those wishing to focus on building a strong foundation of skills employers need, SACA also offers many micro-credentials that allow students and workers to add certifications as they master new areas.
For workers, SACA certifications can help market their smart automation skills to potential employers. For those employers, SACA certifications represent confirmation that a worker has the skills to hit the ground running in the workplace. To learn more about Industry 4.0 certifications and how SACA can help both future workers and industrial employers begin the task of bridging the Industry 4.0 skills gap, contact SACA for more information.
- Published in News
SACA Certifications: Industry’s Missing Link to Solve the Skills Gap
It’s no secret that industries of all kinds are battling a serious supply and demand issue. Due to advancing technology and increasing use of automation, employers need more highly-skilled workers than ever before.
Unfortunately, the supply of workers with the advanced technical and technological skills employers need isn’t keeping pace. This well-known problem is known as the “skills gap.” It’s been a problem for a while now, and experts believe it will only get worse in the near future.
What employers need are workers with advanced “connected systems” skills that will help them operate, maintain, troubleshoot, and repair the automation equipment becoming commonplace in facilities that have adopted new Industry 4.0 technologies.
To date, however, industry and educators alike have been missing the key to solve this skills gap: a set of industry-defined and industry-validated standards that clearly define the skills workers will need to succeed in the jobs of the present and future.
Providing that missing link was the guiding vision behind the creation of the Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA). In a recent webinar (“SACA Webinar”) hosted by Matt Kirchner, President of Lab Midwest, representatives of several major manufacturers spoke about their role in the development of SACA’s Industry 4.0 skill standards, as well as how those standards are now guiding their training and education efforts.
SACA’s Vision for Industry 4.0 Certifications
Why are SACA’s Industry 4.0 certifications so valuable? They speak to the in-demand skills that employers across the country — and across the globe — need so desperately.
Not only do the nation’s educational institutions need to build a pipeline of skilled talent to supply employers with the highly-skilled workers they need now and in the future, but incumbent workers also need training to learn the new skills they need to work with the advanced Industry 4.0 automation systems taking over modern manufacturing facilities.
But what are those skills? That’s the key question, and answering that question is what brought SACA into existence. According to SACA’s Executive Director, Jim Wall:
“SACA’s vision from the beginning was to develop a system that’s based upon industry-developed, industry-validated standards that truly define the competencies, performance indicators, and knowledge indicators that are required of individuals to succeed in the world of Industry 4.0.”
To turn that vision into reality, SACA relied upon a wide variety of companies, educational institutions, and organizations to develop, review, and test SACA certification standards. Experts from well-known industry leaders, such as Rockwell Automation, FANUC, Ashley Furniture, Kohler, Foxconn, Boeing, and Hershey, were instrumental in making sure SACA’s Industry 4.0 certifications reflect the competencies that industry needs.
Industry 4.0 is Here to Stay
Several of the industry representatives who shared stories during the SACA Webinar spoke about the changes that Industry 4.0 technologies have wrought and how their companies have been forced to respond.
Al Doty, Advanced Manufacturing Chief Engineer for Harley-Davidson, Inc., revealed that automation has been key to his company maintaining a competitive edge. Not only do new technologies improve efficiency and reduce costs, but Doty noted that employees also expect the company to adopt and use the best technologies available, so that they can perform their jobs more effectively and maintain a positive work-life balance.
Specific new technologies being adopted include advanced robotics and digital twins, according to Scott Theune, President of Plexus. Digital twins are realtime digital counterparts that allow workers to troubleshoot equipment virtually.
In addition to improving efficiency, these new technologies also play a critical role in making manufacturing facilities safer. Improved safety has been a big benefit as industry growth and the skills gap has spurred the need for more automation, noted Andrew Martin, Senior Director of Manufacturing for Generac.
Leaders throughout industry agree: Industry 4.0 is here to stay. According to Michael DeBroux, Senior Mechanical & Automation Engineer and Engineering Supervisor of Greenheck Fan Corporation, “We need to make sure that we are getting personnel and new talent into our company that speaks modern manufacturing languages and is familiar with Industry 4.0 fundamentals.”
OT and IT are Converging in Industry 4.0
According to an i-SCOOP article, “It’s impossible to talk about the evolutions in manufacturing, industrial transformation and Industry 4.0, innovations in areas such as Industrial IoT without mentioning the convergence of IT and OT.”
Historically, operational technology (OT) has referred to “a category of computing and communication systems to manage, monitor and control industrial operations with a focus on the physical devices and processes they use.”
Information technology (IT), on the other hand, “is about business and enterprise systems that store, process and deliver information.” Because Industry 4.0 technologies are becoming more and more commonplace throughout traditional OT equipment, cybersecurity becomes more critical every year.
According to Jim Molter, IT Manager – Smart Factory Deployment of Kohler Co., “Industry 4.0 is forcing us to break down those silos and start to learn to work together…that’s where we’re headed. There’s not going to be a distinction [between OT and IT] anymore.”
Educational Institutions Play a Key Role in Preparing Industry 4.0 Workers
When experts evaluate strategies for bridging the skills gap, it’s clear that educational institutions must play a key role in preparing students for Industry 4.0 careers. But can they do it alone?
The answer is no. Educational institutions must partner with industry counterparts to ensure that the knowledge and skills they’re teaching will produce students with the valuable skills that industries around the country need.
Anne Troka, Community Engagement Manager for Sargento Foods Incorporated, explains a successful approach she helped to develop called Manufacturing 4.0:
“We started conversations with…four schools and four businesses [to] build a partnership to help students — our future workforce — connect with our businesses to really get skills that we need and skills that the students will need…to make them employable in a variety of different careers, because Manufacturing 4.0 is in manufacturing as well as many other industries.”
To date, the partnership has helped to design and build five courses to prepare students for Industry 4.0 careers, including subject areas like mechatronics, industrial controls, robotics, and the Internet of Things. Eventually, students will also be able to earn SACA certifications related to their coursework. In this way, “we’re really connecting education to [career] success,” concludes Troka.
Industry 4.0 Also Requires Upskilling Current Employees
Unfortunately, employers can’t wait for the next generation of highly-skilled workers to emerge from high school or college. As Anthony Ebio, Director of Industry 4.0 Learning for Ashley Furniture Industries, Inc., noted, schools simply aren’t “cranking out the learning and the students fast enough.”
That’s why Ashley Furniture has invested heavily in upskilling its current employees so that they have the advanced skills they need to work with new Industry 4.0 technologies. Ebio noted that they used SACA certifications as a guide when setting up training for incumbent workers: “We found ourselves leveraging a lot of the SACA structure to make sure that we have [curriculum] to support Industry 4.0.”
Other companies are following suit. Ken Evans, Associate Maintenance Manager for S.C. Johnson & Son, Inc., noted that S.C. Johnson has partnered with Gateway Technical College to upskill its employees with an eye toward achieving SACA certifications.
So far both young and older employees have been excited about the prospect of learning and gaining new skills. Plus, using SACA certifications as a guide has allowed current employees to see a payoff for their hard work quickly. According to Evans, “under SACA, [current employees] can get incremental steps of recognition and be proud of it, and we’re proud of them.”
SACA Brings It All Together
If the current skills gap plaguing industries across the world is to be bridged, strategic partnerships between industry and educational institutions must be forged. Schools must begin to produce a pipeline of highly-skilled workers ready to work in an Industry 4.0 environment.
Likewise, industry must upskill its current workforce with the advanced skills needed to operate, maintain, troubleshoot, and repair the Industry 4.0 automation technologies taking over the factory floor.
According to Michael Cook, Director of Global Academic Partnerships for Platinum SACA Sponsor Rockwell Automation, Inc., “no one company can really do this alone…SACA is providing significant leadership here…ensuring that there’s a close fidelity between the academic space as well as what we find relevant in industry. That alignment is a significant part of what SACA brings.”
To learn more about Industry 4.0 certifications and how SACA can help both educational institutions and industry employers begin the task of bridging the Industry 4.0 skills gap, visit the SACA website and then contact SACA for more information.
- Published in News
Can Smart Manufacturing Transform the Food Industry?
What types of products do you buy online? Today, the answer to that question for many people is just about anything and everything. Things haven’t always been that way, though.
In the earliest days of e-commerce, consumers got their feet wet in the online marketplace purchasing products that were known quantities that could be shipped safely and cheaply. More personal items, such as clothing and shoes, retained a foothold in brick-and-mortar stores where customers could try things on to ensure a good fit.
Fast forward to today and it’s easy to see how drastically e-commerce has changed the retail landscape. Some people now purchase all of their goods exclusively online. There are still certain areas, though, where e-commerce has been slow to gain traction. For example, the food industry has yet to replace a trip to the grocery store with an online experience…until recently.
The COVID-19 pandemic changed much about how we live our lives, including that once-simple trip to the grocery store. Now, more and more people are doing their grocery shopping online or via a smartphone app and having their groceries delivered directly to their car at the store.
As a result, the food industry finds itself in need of a transformation to respond to changing realities driven by consumer demand. Experts believe that transformation will come through a variety of new smart manufacturing technologies.
Consumer Demand Driving Changes
When the COVID-19 pandemic began in early 2020, no one fully understood the ways in which our lives would change over the course of the coming months. Routine, everyday tasks, such as shopping for groceries, were suddenly fraught with the potential for exposure to the deadly virus.
Retail grocers were faced with simultaneously managing intense supply chain disruptions that left many shelves bare and customers who wanted as little contact with other shoppers as possible. The solution for many was to pair online shopping (often via an app) with curbside delivery.
Shopping for food online was a new experience for most customers. It didn’t take long, however, for most people to figure out that they could compare prices across various stores just like they would for any other online purchase.
The effect of these changes on the food industry has been significant. As author Katy Askew notes in a recent FoodNavigator article, the food industry is being forced “to rapidly adapt their processes and products to keep up with changing markets” resulting from “elevated consumer expectations.”
Smart Manufacturing to the Rescue
How can food and beverage companies keep up with these rapid changes? Askew spoke with Andrew Smith, Regional Segment Leader – Process & Packaging OEMs at Rockwell Automation, which recently became a Platinum Member of the Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA).
According to Smith, “To remain competitive, food and beverage manufacturing systems must optimize productivity and perform at the highest standard. This requires comprehensive and continuous operations improvement.” Increasingly, the food industry is turning to smart manufacturing to achieve those goals.
Smith believes in the potential of smart manufacturing:
“Connected, information-enabled manufacturing – or smart manufacturing – can make all the difference. New technologies are helping food and beverage manufacturers better understand and use their food processing operations. Smart manufacturing can help improve asset utilization, increase yield, drive workforce productivity, optimize resource management, and mitigate security risks.”
Not convinced yet? Smith points to Hillshire Brands as a prime example of what smart manufacturing can do. After the company began using a manufacturing intelligence system at a Texas plant, “the food manufacturer reduced inedible product and waste goals to 0.8% – saving about 5.5 million corn dogs per year.”
Technologies Changing the Game
The impact of smart technologies is not lost on the average person today. Whether it’s the smartphone in your hand or the smart thermostat keeping your home the perfect temperature, nearly every aspect of life has been impacted by advances in technology
Modern manufacturers are no exception, including food and beverage companies. According to Smith, “New developments in technology are redefining food and beverage manufacturing. By combining the Internet of Things, wireless and mobile technologies, data analytics, and network infrastructure, companies can access and act on the data from their operations before a potential problem arises.”
Askew notes in her article that Smith identified five advanced technologies he believes will drive greater adoption of smart manufacturing technologies in the food industry:
Flexible Manufacturing
Flexible manufacturing focuses on how quickly a company can adapt to change. As Matt Graves and Rachel Wilson explain in an article on the Rockwell Automation blog, “It’s about creating a seamless flow from need to delivery. True flexibility empowers manufacturers to stay in tune with their market, by replacing rigid and static operating models with levels of control and responsiveness never previously thought possible.”
When it comes to integrating new technologies, though, the authors stress that companies must not forget about the people using those technologies:
“When it comes to embracing Industry 4.0, integration between departments is key. While new technology can bring data and systems together, getting your people to communicate/collaborate is just as important – and absolutely essential if you want to gain the maximum return on investment.”
Augmented Reality
As Askew notes in her article, “Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that allows users to view and interact with real-world environments through computer generated superimposed images. It enables workers to perform better and avoid safety and compliance risks by providing easy access to the information they need online.”
In smart manufacturing, companies use AR to help technicians troubleshoot problems in real time. For example, maintenance personnel can use an AR app on a smartphone or tablet to zero in on exactly what component of a machine may be malfunctioning and develop a solution more quickly, thereby reducing equipment downtime.
Predictive Maintenance
The heart of smart manufacturing is the collection, processing, analysis, and application of the tremendous amounts of data (sometimes called “big data”) generated by the production process. According to Askew, companies will use “powerful machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics software to offer predictive and prescriptive maintenance.”
Practically, this means that machines equipped with smart sensors can monitor their own performance. Technicians will receive alerts from machines when maintenance needs are imminent, allowing them to maintain and repair equipment before breakdowns occur, thereby reducing downtime and increasing productivity.
Edge Computing
A Rockwell Automation article explains edge computing in this way:
“Edge computing combines a machine’s control and computing hardware into one platform, either with a controller that has a built-in computer or with a computing module that sits on the same rack as the controller. With this two-in-one approach, you can put all your machine’s digital content — such as custom code, the controller’s human-machine interface (HMI) application and any third-party software programs — right where the controller resides, rather than in another location. This creates inherent benefits for end users, including space savings and access to data right at its source. But it also creates new opportunities for you to build entirely new solutions for production applications.”
According to Askew, “Edge computing will complement existing cloud infrastructure by enabling real-time data processing where work is done (for example, motors, pumps, generators, or other sensors). Implementing integrated analytics from the edge to the cloud will help these companies maximize the value of investments in digital systems.”
Digital Twin/Digital Thread
In addition to augmented reality apps, companies are also using advanced digital tools to assist with troubleshooting, such as digital twins and the Digital Thread. According to Askew, a digital twin is “the collection of data created in software representing a real-life system. Machines, controllers, processes, workflow, and any other aspect of a system can be represented digitally, without any interruption to ongoing activities.”
Similar to a digital twin, the Digital Thread “creates a virtual representation of how data travels within a company. The Digital Thread enables supervisory enhancements throughout the supply chain, including delivery of work instructions to operators, quality control sampling, and automated activation of components and materials from vendors, suppliers, and partners”
What can these technologies do for the food industry? Askew paints an interesting view of a future that’s probably a lot closer than we think:
“In the near future, we will see that by interconnecting business systems through the Digital Thread, companies will practically start up new production lines. Using the digital twins, manufacturers will run machines virtually before parts are ordered, discover control issues before support personnel review them, predict future performance challenges and opportunities, simulate line changes to stay keep up with changing customer demands, and will train new staff in non-stop systems of activity.”
SACA Certifications Validate Industry 4.0 Skills
Employees in the food and beverage industry would do well to complement their current skillset with advanced Industry 4.0 skills that will help them change and grow with advances in technology. For those workers wanting to specialize in Industry 4.0 technologies, the certifications offered by the Smart Automation Certification Alliance are a great place to start. SACA offers industry-standard certifications that focus on “connected systems” skills. To learn more about the different types of SACA certifications, visit SACA online.
- Published in News
Top 5 Future Smart Automation Careers in Manufacturing
Oh, how five years can change things.
Turning the clock back all the way to 2015, gasoline had fallen under $3 nationally for the first time in four years, NASA was confirming the presence of water on Mars, and the smash-play Hamilton was the hottest ticket on Earth (you know, back when we could still go to concerts…).
Even manufacturing of those times now feels slightly antiquated. Promises of big data driving efficiency and predictive maintenance technologies, which were introduced on a national scale in 2015, are now commonplace around Smart Factories. Today, more efficient strategies are practiced by companies, leading to a manufacturing boom – another prediction-come-true from 2015.
While we could spend time reminiscing about the “ol’ days”, innovation doesn’t take a break. With more products being created daily than we’ve ever experienced before, it only makes sense for manufacturing to keep focused on improving production for future endeavors.
And it begs the question: where do we see manufacturing five years from now? Based on its history, changes are expected, according to Deloitte. Specifically, they predict several important themes will be reflected in these changes, including:
- Putting Humans in the Loop: Organizations are working harder to keep humans in the loop, such as rethinking work architecture, retraining people, and rearranging the organization to leverage technology. The hope is to not only eliminate routine tasks and cut costs, but create value for the customers (and meaningful work for the employees).
- Expanding Digital and “Soft” Skills: Despite the rise of automation, and technology replacing many mundane tasks, manufacturing requires human workers to ensure that everything runs smoothly. The essential human skills deemed most useful over the next decade include critical thinking, creativity, and people management.
- Leveraging the Digital Toolbox: Manufacturing workers are becoming more reliant upon digital tools, such as collaboration platforms, work-based social media, and instant messaging, to effectively complete their work.
In addition to these themes, Deloitte also anticipates five future skillsets that each manufacturing worker should possess, including being proficient in: Technology / Computer, Emerging Digital Technologies, Programming for Robots / Automation, Working with Tools and Technology, and Critical Thinking.
So how can these themes and skills work in combination to create future jobs?
According to Deloitte:
“As digital transformation and the Fourth Industrial Revolution continue to redefine manufacturing jobs of the future, leaders and workers alike need to embrace a work environment that is expected to blend advanced technology and digital skills with uniquely human skills, to yield the highest level of productivity. Understanding how work might change can help the industry as a whole prepare for a future that promises to be transformative.”
With that transformative future comes a new onslaught of smart careers – many of which have been created as a direct correlation to the ever-changing industry. In this article, we will highlight five of the jobs that Deloitte has tabbed as the most promising future smart automation careers in manufacturing, as well as what that position could potentially look like.
Job #1 – Digital Twin Engineer

SUMMARY: A digital twin engineer creates a virtual representation of both the physical elements, as well as the dynamics of how an IoT-connected product operates and interacts. Simply put, a digital twin engineer makes it possible to virtually see inside any physical asset, system, or structure to optimize design, monitor performance, predict maintenance, and improve the overall experience.
Used throughout a wide range of industries, digital twin engineers rely upon their engineering tooling to integrate necessary digital elements to produce the high-quality product. In addition, they act as a working link between the product twin and the performance twin, which can help enhance collaboration with customers, accelerate innovation, design smarter products, and create new services.
RESPONSIBILITIES: Using 3D software and simulations, a digital twin engineer will create digital twins to measure product performance throughout a variety of conditions. The insights discovered through the data help design new products and business models. Engineers also use machine learning, real-time usage, and performance data to optimize product performance and service.
SKILLS NEEDED: In creating virtual replicas of major industrial products, as well as helping companies predict and respond to customer problems using real-time data analysis, digital twin engineers need to be well-versed in simulations, analytics, and software development. Systems engineering, as well as research and development, are also critical.
Job #2 – Smart Factory Manager

SUMMARY: A smart factory manager is a jack-of-all-trades, so to speak. From production and quality, to IT and cyber responsibilities, a smart factory manager takes on an expanded, and often times unique, role of integrating advanced manufacturing, securing connectivity, and understand data analytics to drive a new level of overall equipment effectiveness, or OEE.
The goal of the smart factory manager is to identify data patterns that can help predict quality issues, as well as direct actions in response to these insights. In addition, they will leverage predictive maintenance analytics to identify issues before they happen, and direct preventative maintenance to address future issues.
RESPONSIBILITIES: A smart factory manager must be able to identify and aid in the addition of advanced technologies that enable self-optimization. They must be able to build a variety of automated manufacturing capabilities, such as robot cutting, 3D printing, and more. Finally, they are responsible for managing the installation, operations, and maintenance of all levels of the smart factory solutions “stack” that delivers continuous connectedness and ensures cybersecurity protocols are followed.
SKILLS NEEDED: Being skilled in applied technology, automation, and connectedness are a must for smart factory managers. In addition, operational excellence, deep learning, and innovation are also key to finding success in the field. Digital prototyping and client management are also plusses.
Job #3 – Robot Teaming Coordinator

SUMMARY: With increased automation comes a larger need for robots. And robots, like any other industrial component, needs to be able to effectively perform its predetermined tasks. As a Robot Teaming Coordinator (RTC), it is their task to oversee robots that interact with humans to enable a human rapport with robots, ensuring optimal human-machine interactions.
Generally, the RTC is responsible for monitoring robot performance, and giving feedback to programmers to perfect robot value. However unlike robot programmers, a robot teaming coordinator are often not experts in programming languages, but should have the knowledge to understand how robots are supposed to behave in work environments.
RESPONSIBILITIES: In addition to observing and evaluating robot performance, an RTC is responsible for sharing its feedback with robot programmers, recommending areas for improvement. They will train human team members to help them work more collaboratively with robots, as well as work in tandem with robot coordinators from other departments to identify opportunities to enhance productivity. Finally, all of those results are delivered against key performance indicators to view overall customer experience, improvements in productivity, and more.
SKILLS NEEDED: An RTC needs to be proficient in robot behavioral analysis by enabling a collaborative human-robot working environment, which applies a mixture of digital, social, and human skills to help humans and robots leverage each other’s strengths and improve productivity. This means a robot teaming coordinator needs to be well-versed in human-machine collaboration, as well as robot management.
Job #4 – Smart Safety Supervisor

SUMMARY: In most workplace environments, safety is the number one concern. That’s no different in a Smart Factory – only this time, it’s the Smart Safety Supervisor who is responsible for overseeing proper safety procedures are being utilized. A Smart Safety Supervisor works with operational, logistics, and technology teams to ensure safety, as well as finding new synergies that can improve the safety of workplaces.
With Smart Factories dealing with autonomous equipment, unmanned drones, and advanced materials, a Smart Safety Supervisor needs to be fluent in advanced technologies, and match those applications – such as smart helmets or augmented reality (AR) glasses to help create a safe and efficient work site. They will also use their broad knowledge of regulations, Environment, Health & Safety (EHS) standards, and available technologies to help companies develop technology implementation road maps, or help leverage the digital twin of a construction site to oversee health and safety of workers and machines.
RESPONSIBILITIES: When it comes to keeping workers safe, a Smart Safety Supervisor has a laundry list of responsibilities. From identifying new technologies to meet set safety targets, to formulating safety procedures and plans to reduce potential safety hazards, a Smart Safety Supervisor will be responsible for taking all of the necessary steps to ensure workplace safety. The job also includes incorporating specialized risk management principles between machines and humans, supervising safety specialists, and acting as a field safety inspector on incident investigations.
SKILLS NEEDED: The most necessary skill is having an advanced working knowledge of construction safety, safety management systems, and occupation and health regulations. Smart Safety Supervisors are skilled in EHS, workplace inspection, and risk assessment, as well as understanding digital tools and technologies to aid in keeping everyone safe. Finally, having experience developing and implementing multiple health and safety programs for various projects is a plus.
Job #5 – Smart QA Manager

SUMMARY: A “smart quality assurance (QA) manager” manages product quality using digital technologies. That means a smart QA manager will oversee an ecosystem of machines and work center sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), and virtual reality (VR) support technologies to proactively detect quality escapes and machine maintenance issues, as well as develop solutions to address those root causes of quality issues.
From developing requirements for AI and machine-learning (ML) algorithms that identify products defects as early as possible, to reducing the number of defects per part produced, the main task of a smart QA manager is to minimizes production downtime, and maximize productivity by reducing manual inspection.
RESPONSIBILITIES: A smart QA manager will be looked upon to work with the facility manager to develop and maintain the production schedule, as well as plotting historical data to develop predictive quality controls and detection algorithms. In addition, they will be responsible for conducting quality issues root cause analysis, providing corrective actions, and identifying new technologies to incorporate into QA systems.
SKILLS NEEDED: An experienced QA manager is trained in leveraging smart technologies to reduce the number of defects per part produced, with goals to enhance overall productivity. Other useful skills include operational excellence, innovation, automation, and digital prototyping. Like all future smart positions, it also requires a passion for deep learning.
Need Help Certifying Your Workforce for Smart Automation? Consider SACA!

With all of these future careers on the horizon, industry-endorsed Industry 4.0 certifications will become even more valuable. That’s why the Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA), a non-profit organization, has made it our mission to develop and deploy Smart Certifications for a wide range of industries.
Thanks to the help of our partners, SACA has created certifications that are industry-driven, developed for industry by industry. They are developed through a rigorous process that begins with the creation of truly international skill standards, endorsed by leading experts in Industry 4.0 technologies throughout the world.
SACA’s Smart Automation certifications use a modular structure to enable them to fit a wide range of individual needs, industries, and educational environments, and are available in three categories – Associate, Specialist, and Professional. Each certification is stackable, allowing individuals to start with one certification and add other certifications to customize their documented skills.
All SACA certifications are occupationally focused, so they prepare individuals for specific careers in the world of Industry 4.0. If you would like more information into SACA’s world-class Smart Certifications, please visit our website!
- Published in News
Industry-Recognized Apprenticeship Programs: IRAPs Promise New Opportunities
LOUISVILLE, KY—OCTOBER 14, 2020
Industries across the United States have been struggling for years to fill open positions with qualified workers. Despite widespread recognition of the problems industries face, the skills gap has continued to widen.
Rather than bringing new solutions, 2020 instead saw a global pandemic make an already-tough jobs situation worse. Due to the COVID-19 crisis, millions of American workers have lost their jobs, many of them permanently.
As the U.S. seeks to recover from “the most devastating economic crisis since the Great Depression,” there is no shortage of problems that must be addressed and solutions that need to be formulated. How effective those solutions are will dictate the speed and scope of economic recovery.
Unlike past economic recovery initiatives that often pushed people toward college degrees, experts believe that our current economic recovery from the COVID-19 Recession must instead focus on practical skill development for jobs industries need. To that end, community colleges and skills training may play a critical role.
Another potential solution with a proven track record of success is apprenticeship. In fact, many believe new industry-recognized apprenticeship programs (IRAPs) will provide fresh opportunities for both American workers and industries that desperately need skilled talent. How? IRAPs will expand the use of the apprenticeship model to industries that haven’t used it or have underutilized it in the past.
What Are IRAPs?
So what exactly are IRAPs anyway? According to the U.S. Department of Labor’s (DOL) Apprenticeship.gov website:
“Industry-Recognized Apprenticeship Programs are high-quality apprenticeship programs recognized as such by a Standards Recognition Entity (SRE) pursuant to the DOL’s standards. These programs provide individuals with opportunities to obtain workplace-relevant knowledge and progressively advancing skills. IRAPs include a paid-work component and an educational component and result in an industry-recognized credential. An IRAP is developed or delivered by entities such as trade and industry groups, corporations, non-profit organizations, educational institutions, unions, and joint labor-management organizations.”
For example, the Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA) was recognized as one of 18 initial organizations designated as an SRE by the DOL on September 23, 2020. SACA may now evaluate and recognize IRAPs consistent with DOL standards.
What are those standards? According to the DOL’s IRAP Fact Sheet, high-quality IRAPs must meet the following 10 requirements:
- Paid Work
- Written Training Plan
- Written Apprenticeship Agreement
- Specialized Knowledge and Experience
- Safety
- Equal Employment Opportunity
- Credit for Prior Knowledge
- Mentorship
- Industry-Recognized Credentials
- Disclosure of Costs and Fees.
When Were IRAPs Created?
IRAPs are a relatively-new solution in the area of workforce development. Their history can be traced back to June 15, 2017, when President Trump issued an Executive Order to Expand Apprenticeships in America.
According to a DOL press release, the order established the 20-member Task Force on Apprenticeship Expansion, which was “headed by the Secretary of Labor and co-chaired by the Secretaries of Commerce and Education.”
The DOL’s IRAP Fact Sheet notes that the president’s order “directed the Secretary to consider proposing regulations that promote the development of apprenticeship programs by third parties…especially in sectors where apprenticeship programs are insufficient.”
The Task Force subsequently recommended the establishment of IRAPs in May 2018. Eventually, as the IRAP Fact Sheet notes:
“To address America’s skills gap and to rapidly increase the availability of high-quality apprenticeship programs in sectors where apprenticeship opportunities are not widespread, the [DOL] has issued a Final Rule that establishes a system for advancing the development of high-quality IRAPs.”
IRAPs then became official when new regulations took effect on May 11, 2020.
How Do IRAPs Differ from Traditional Apprenticeships?
According to a recent Forbes article by Ryan Craig:
“For years, policy makers have struggled with the question of how to expand apprenticeships from traditional blue collar building and industrial trades to fast-growing sectors like technology, healthcare, and professional services. On a per capita basis, the U.S. is far behind other nations: Germany has nearly 20x as many apprentices, and the UK has 14x.”
Craig further notes that the goal of IRAPs is:
“to increase the number of actual American apprentices from 500,000 to 5 million by decentralizing apprenticeship authority from the DOL to hundreds of third party IRAP authorizers [SREs]…The expectation is that while DOL registered apprenticeships are infamous for the amount of paperwork required, IRAPs will be much less onerous and therefore more popular.”
Rather than taking apprenticeships in an entirely new direction, IRAPS are “intended to run in tandem with the department’s long-established registered apprenticeship program,” according to an article from the Community College Daily website. Indeed, the DOL’s IRAP FAQ clearly notes:
“IRAPs and RAPs [Registered Apprenticeship Programs] will work on parallel tracks with the support of the Department. The Registered Apprenticeship system has produced successful results in many industries for over 80 years and it will continue to do so. The industry-led, market-driven approach outlined in the IRAP final rule will give employers and other stakeholders the additional flexibility necessary to expand the apprenticeship model into new industries where registered programs are less prevalent and to address the diverse workforce needs of different industries and occupations. IRAPs provide a new apprenticeship pathway that lets industry organizations take the lead in identifying high-quality apprenticeship programs and opportunities based on the needs in their industry.”
Consistent with the goal of expanding the apprenticeship model to new industries, one notable difference between IRAPs and RAPs is that SREs are prohibited from recognizing IRAPs in the construction industry. According to article by Katie Spiker from the National Skills Coalition:
“This carve out was…the subject of a massive campaign by the building trades unions…According to proponents of the construction industry exclusion, and the Department in their justification of excluding construction in the final IRAP rule, the fact that the majority of U.S. apprenticeships are in the construction industry is evidence the model is effective for the industry and that expanding IRAPs to construction is not necessary to meet the goal of expanding apprenticeships in the U.S.”
Who Will Benefit from IRAPs?
The DOL clearly outlines a set of expected benefits to both workers and businesses in its IRAP Fact Sheet. For businesses, the DOL expects IRAPs to:
- provide an additional pathway to assist career seekers and job creators;
- serve the needs of business by expanding apprenticeships across more industries;
- use innovative, industry-driven approaches to scale a proven workforce education model;
- allow more flexibility to design apprenticeship programs that meet business needs; and
- supply an immediate pool of workers for today and skilled talent for tomorrow.
For workers, IRAPs are expected to:
- offer opportunities to earn and learn, while obtaining valuable, portable, industry-recognized, competency-based credentials;
- provide training in standards that are developed by the industry, ensuring an apprentice develops the skillset needed for career success;
- increase the opportunities for apprenticeship programs across all sectors in the economy; and
- provide an alternative to college for finding career success that allows workers to obtain high paying jobs without going into debt.
Katie Spiker echoes the view that both workers and businesses should benefit from IRAPs: “The IRAP initiative is evidence of the need to modernize apprenticeship, expand access to workers to earn industry-recognized credentials and allow businesses to play more of a role in helping tailor the kind of training their workers receive to meet their specific needs.”
While traditional registered apprenticeship programs have been successful for years, Roy Maurer notes in a recent article for SHRM, the Society for Human Resource Management, that “only about 0.2 percent of the U.S. workforce has taken advantage of the programs, primarily in trades and construction.” The DOL believes IRAPs “will effectively expand apprenticeship in telecommunications, health care, cybersecurity and other sectors where it’s currently not widely used.”
Rachel Greszler, senior policy analyst at The Heritage Foundation, believes the benefits to workers are clear:
“The [IRAPs] rule is an important step in opening up more nontraditional and affordable education opportunities that could particularly benefit younger Americans who have been left behind by America’s higher-education system, as well as current workers who have been negatively impacted by changes in industry and technology. It’s not in everyone’s best interest to pursue an expensive four-year college education, and these types of apprenticeships make it possible for individuals to obtain the education they need for a promising career without taking on debt, and instead, actually being paid in the process.”
As U.S. Labor Secretary Eugene Scalia summarized in a DOL press release:
“As workers seek to reenter the workforce following the economic disruption caused by coronavirus, [IRAPs] and the SREs that recognize them will provide new opportunities for Americans to earn a living while learning the skills needed in a changing job market.”
Where Can I Learn More About IRAPs?
According to Ryan Craig:
“There are millions of unemployed workers whose jobs are unlikely to return once the pandemic subsides. So one of the most important policy questions in America today is how they’ll find paths back to work…If there is an answer, apprenticeships will almost certainly play a leading role.”
If you want to learn more about IRAPs and the SREs who will be helping to bring them to life, be sure to check out the DOL’s Apprenticeship.gov website. The latest information and developments will be posted there as IRAPs take shape and begin to fulfill the goal of expanding apprenticeships into new industries while helping workers gain new skills.
- Published in News
Macomb Community College Joins SACA to Provide Students with Industry 4.0 Certifications
LOUISVILLE, KY—AUGUST 17, 2020
The Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA) is pleased to announce that it has recently entered into an agreement with Macomb Community College and ATS Midwest to support the college’s efforts to align its education and training to meet the realities of Industry 4.0. Students completing Macomb’s advanced manufacturing programs will soon earn SACA certifications, giving them a competitive advantage in today’s job market.
Today’s students face a far different world of advanced manufacturing than existed a decade ago. While automation technologies have been commonplace for many years, the Internet has brought about a convergence of new “connected” technologies that is revolutionizing how products are made.
Known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution or Industry 4.0, this latest disruption of the advanced manufacturing world is resulting in reduced downtime and increased quality, productivity, and overall efficiency in industries of all kinds thanks to advanced technologies that make up what is known as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
IIoT technologies include such things as advanced robotics, machine learning, artificial intelligence, autonomous vehicles and machines, cloud-based data analysis, and cybersecurity. As companies increase their use of networks and Internet technologies, they are connecting more devices, from smart sensors to smartphones.
As a result, these highly-connected systems require new skills in almost every occupation. To succeed in an Industry 4.0 environment, current workers and today’s students must learn to interact with software, data, networks, and smart devices.
While there are many certifications available today that address isolated competencies, from machining to maintenance and information technology (IT), SACA certifications are different. SACA’s Industry 4.0 certifications certify “connected systems” skills that address the integration of the many types of advanced manufacturing technologies with Industry 4.0 technology.
SACA’s Industry 4.0 certifications have been developed for industry by industry through a rigorous process that began with the creation of truly international skill standards. These standards have been endorsed by leading experts in Industry 4.0 technologies around the world.
Working with forward-thinking institutions like Macomb will enable SACA to accomplish its vision to provide highly-affordable, accessible Industry 4.0 certifications that significantly increase the number of individuals who possess the skills represented by these credentials.
The result will be an increasing number of students prepared to be successful in an Industry 4.0 world, as well as more companies that have the highly-skilled workers they need. Don Hutchison, Macomb’s Dean of Engineering and Advanced Technology, agrees:
In southeast Michigan, industry already needs employees who understand how advanced manufacturing systems integrate. At Macomb, we are listening to industry and creating training for individuals and industry that meets the challenges and opportunities of Industry 4.0. Arming Macomb’s graduates with SACA certification signifies to employers that they are prepared to successfully navigate the complex, integrated nature of today’s manufacturing environment.
Fortunately, Macomb also enjoys the support of local industry. Tom Kelly, Executive Director and CEO of Automation Alley, Michigan’s leading manufacturing and technology business association and Industry 4.0 knowledge center, supports Macomb’s vision:
It is encouraging to see Macomb Community College commit to Industry 4.0 training, which will help to ensure industry receives graduates with employable skills. Today, technology is moving at an accelerated pace which requires a new set of working skills. If our state is to keep pace and maintain a global leadership position in manufacturing, we must transform and continuously develop our talent pipeline.
SACA looks forward to a long relationship with Macomb as they, together with industry partner ATS Midwest, begin a thorough review of all of the college’s advanced manufacturing programs to ensure SACA certification requirements are incorporated into the programs’ core curricula. The parties will also be reaching out to local industry to confirm that SACA certification requirements reflect the skills needed by industry. For more information about SACA and how its Industry 4.0 certifications can prepare your students for the jobs of the future, visit SACA.org or contact SACA Executive Director Jim Wall.
- Published in News
Indiana Governor’s New Initiative Offers Free SACA Silver Certifications for Hoosiers
During Indiana Governor Eric Holcomb’s June 5, 2020 press conference, a new state initiative was announced that will offer 10,000 free credentials to Indiana residents that have been dislocated from their jobs due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA) is one of the organizations offering credentials to displaced Hoosier at no cost. SACA’s certifications are task-based and nationally recognized in preparing individuals for rewarding careers working with advanced manufacturing and Industry 4.0 technologies.It’s no secret the immense role that Industry 4.0 is expected to play in the future of industrial manufacturing.
These courses can be taken online and feature virtual simulation of industrial applications, which make them ideal for preparing users for the workplace. The online delivery also allows users to practice social distancing guidelines to help prevent the spread of Coronavirus.
Ivy Tech will coordinate enrollment of new students while Amatrol and Aidex will help to promote this opportunity to displaced Indiana residents seeking a new career path. Amatrol will also provide free access to its Learning Management System (LMS) for students enrolled in this program.
When a student completes one of the six courses, they will be eligible to sit for the associated SACA Silver Credential. SACA Silver Credentials are completed solely online while Gold Credentials involve hands-on skill demonstrations. Students are eligible to earn all six SACA Silver credentials.
People interested in these opportunities can visit YourNextStepIN.org, which is part of Indiana’s Rapid Recovery for a Better Future initiative. Lubbers said, ““Visitors to the site can talk to a real person to answer questions and help them determine the right path forward and the training options that will help them achieve their goals. These partners and tools help to connect Hoosiers to opportunities — some that already exist — and we will continue to build on these connectors in the weeks and months ahead.”
The free courses and associated SACA Credentials are as follows:
Production Operations Technician
- Certified Industry 4.0 Associate I (C-101): Students will study Industry 4.0 concepts, safety, quality, technical drawings, machine operation and maintenance, and hand tools.
- Certified Industry 4.0 Associate II (C-102): Students will study manufacturing systems performance, mechanical and fluid power systems, programmable controller systems, CNC and additive manufacturing, system communications, and mechatronics.
Multi-Skill Maintenance Technician
- Electrical Systems 1 (C-201): Students will study electrical system safety, electrical schematics and diagram, taking electrical measurements using a digital mustimeter (DMM), combination circuits, electrical circuit troubleshooting, and inductive and capacitive circuit analysis.
- Electric Motor Control Systems 1 (C-202): Students will study electric motor safety, ladder logic schematics, how to properly ground connections, transformer selection and installation, how to connect and operate a 3-phase motor, and how to connect and operate a variety of electric motor circuits including manual motor, 2/3 wire magnetic motor starter, reversing motor control, hands-off-auto motor control, and basic timer control.
- Motor Control Troubleshooting 1 (C-204): Students will study how to troubleshoot motor control components, use a clamp-on ammeter to measure motor current, and troubleshoot a variety of motor control circuits and an AC VFD motor control system.
- Pneumatic Systems 1 (C-209): Students will study pneumatic system safety procedures, pneumatic schematics interpretation, how to connect and adjust pneumatic supply lines, how to start up and shut down a reciprocating air compressor, how to connect and operate basic pneumatic circuits, how to monitor system operation, pressure and force, and how to perform basic system servicing.
- Published in News

The Importance of a Smart Automation Certification
- Published in News
Smartphones, Smartwatches, & Now Smart…Factories?
Did you ever have math teachers who were real sticklers for knowing the fundamentals? Frequent reminders to “show your work” were likely accompanied by the admonition that “you’re not always going to have a calculator in your pocket!”
Well, I guess we showed them didn’t we? The smartphones that occupy our pockets today not only have a calculator, a telephone, a calendar, a map, an address book, a clock, a camera, and a music player, they also contain a nearly-limitless variety of applications that give us access to data and capabilities unimaginable a generation ago.
Your smartphone might connect to a smartwatch that keeps track of your heart rate while you read emails on the go. It might also connect to a variety of smart home devices, allowing you to turn on light bulbs, answer the doorbell, and lower the thermostat from anywhere in the world.
The Internet of Things (IoT)

All of these so-called “smart” devices are part of what’s now known as the “Internet of Things” (IoT). The IoT allows a wide variety of devices to connect and communicate using the Internet, making life more convenient in ways many people never dreamed possible.
There are now even voice-activated assistants ready to do our bidding. Today, a call of “Hey Siri!” or “Hey Alexa!” might be followed by a command to turn on the outside lights at home, an inquiry about the state capital of Wisconsin (it’s Madison, by the way), a request for the latest weather forecast, or an appeal for a quick eggs Benedict recipe.
Our lives have been forever transformed by the IoT. Today’s youth have grown up in a world of connected devices. Even older adults, though, now use these devices and understand their benefits. Many of us see how they make our day-to-day lives easier, but do we fully realize how they will impact our jobs, both now and into the future?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution
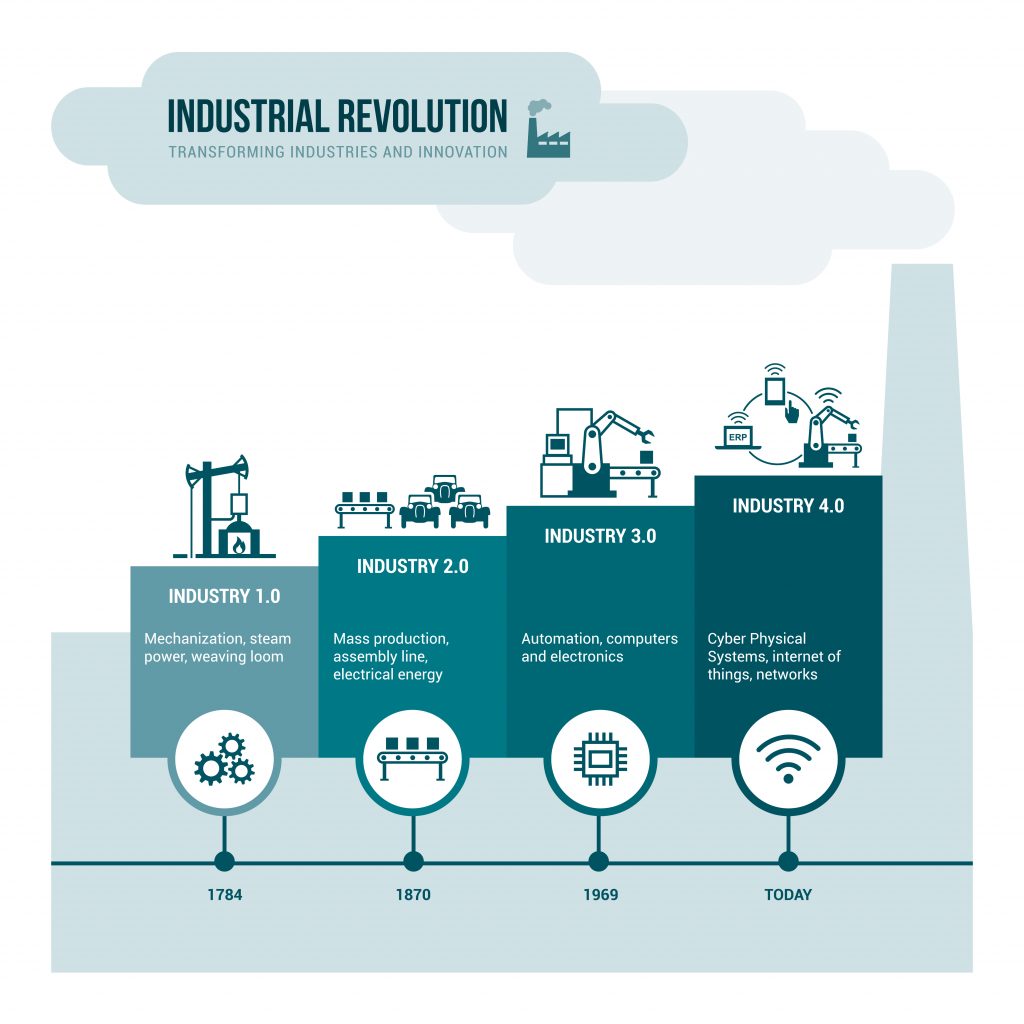
History buffs will remember that the Industrial Revolution began in the second half of the 18th century when manpower began to be replaced by machines powered by steam or coal. What many people don’t realize, however, is that scholars have identified subsequent revolutions in industry.
The Second Industrial Revolution got its start in the first half of the 19th century when electricity combined with the assembly line to allow mass production. A Third Industrial Revolution traces its roots to the 1950s when the digital age was born with the advent of the first computers and the beginnings of automation.
Today, we find ourselves in the early stages of the Fourth Industrial Revolution when cyber-physical systems, automation, and the IoT will combine to create a Smart Factory environment that holds the potential for a massive impact on industrial efficiency and productivity.
Whatchamacallit
This new Fourth Industrial Revolution goes by a variety of names and terms: Smart Automation, Smart Factory, Smart Manufacturing, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), the Industrial Internet, the Connected Enterprise, and Industry 4.0, to name a few. Whatever you choose to call it, it’s both the wave of the future and the present reality.

Smart factories already exist, and they’re getting bigger and better every day. Industry 4.0 pioneers in a wide variety of industries are forcing competitors to embrace Smart Automation as a tool to take them to the next level.
Inside the Smart Factory

What is a Smart Factory like? Envision a facility in which self-driving vehicles communicate with production-line robots to request and deliver necessary parts without human intervention. Imagine these connected machines on the production floor communicating with workers on the top floor to convey a wide variety of information, such as production cycle times, mechanical breakdowns, and predictive maintenance.
Smart robots and machines equipped with smart sensors can generate a virtually-unlimited amount of data (often referred to as “big data”) that can be shared with multiple locations via cloud technology. This data can be used not only to monitor real-time production status but also to predict future maintenance needs. Can you imagine a robot continually analyzing its productivity and condition, so it can order replacement parts or other maintenance needs before it breaks down?
The Skills Gap

At one time, many workers feared the day when robots would replace humans in the workplace. Some still do. However, the reality of Industry 4.0 is quite different. While it’s true that robots and automated machines have replaced some jobs, the advanced technologies required by Industry 4.0 have and will continue to generate a tremendous demand for highly-skilled workers to program, analyze, and maintain the many parts of these complex systems.
That sounds fantastic until you realize that industry experts believe there’s a tremendous shortage of workers qualified to fill these positions. According to a recent study by Deloitte, nearly 3.5 million manufacturing jobs will need to be filled in the next decade. Because of what is commonly known as the “skills gap,” however, experts estimate as many as 2 million of those jobs could go unfilled.
Training for a New World

Despite the fact that we live in a connected world and understand its benefits, many people still lack the skills they will need to thrive in an Industry 4.0 environment. While many people have embraced advanced technology in their personal lives, they lack real-world exposure to manufacturing equipment and processes.
To prepare students and current workers for careers in smart factories, educators and companies must teach skills in a variety of areas, including industrial equipment and technology, smart sensors and smart devices, computerized control systems, network security, and data collection and analysis. Experience with real-world equipment and access to state-of-the-art training will be critical.
SACA’s Vision

Once you gain experience and receive the training you need, how will you market yourself to employers? How can you easily demonstrate to others the skills, experience, and training that you possess?
The Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA) offers highly-affordable, accessible Industry 4.0 certifications for a wide range of industries. While many certifications are available today that address isolated competencies, from welding and machining to maintenance and IT, SACA certifications are different. They certify “connected systems” skills that address the integration of these technologies with Industry 4.0 technology.
SACA’s vision is to provide certifications that significantly increase the number of individuals who possess the skills represented by these credentials. This will ensure that companies have the highly-skilled workers they need, and individuals are prepared to be successful in Smart Factory jobs that require certified “connected systems” skills.
- Published in News